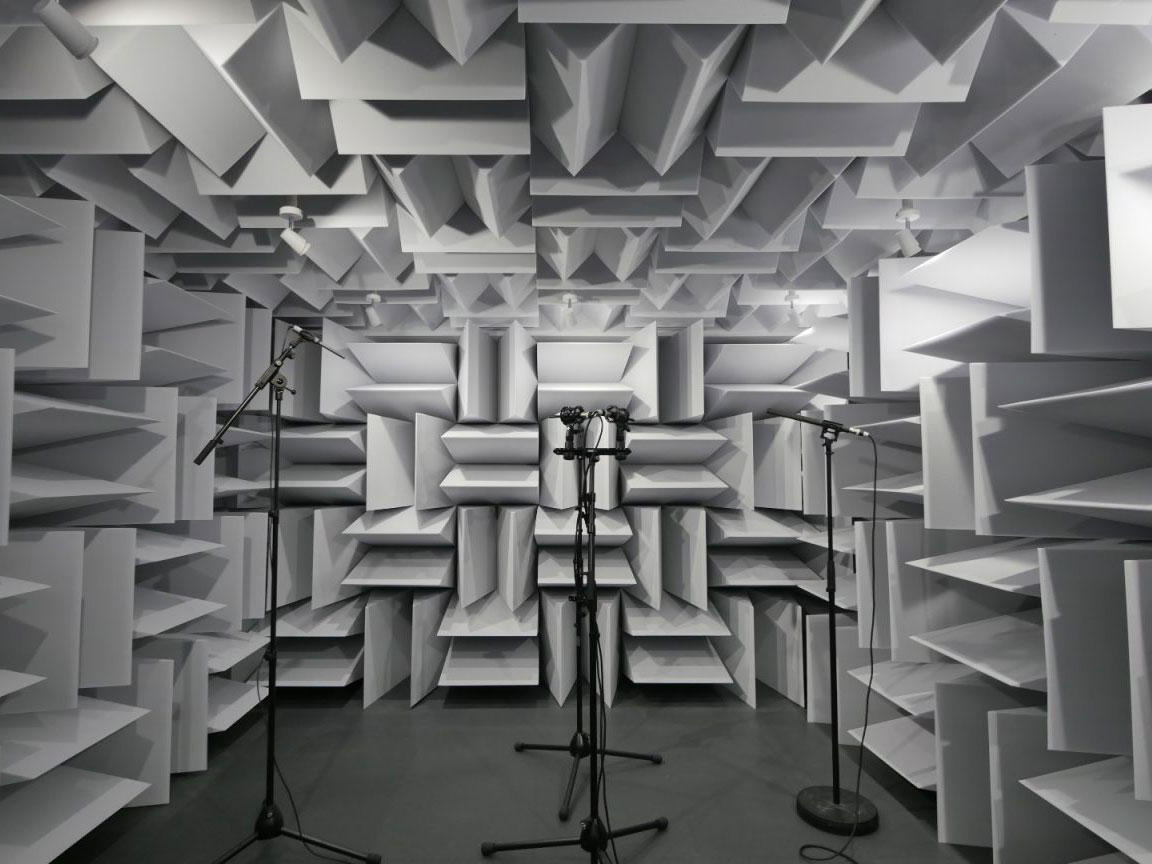

Introducing DXOMARK’s semi-anechoic chamber
9 April 2020, Paris – We are pleased to unveil our new anechoic chamber—a project that took nearly six weeks and nine tons of materials to realize. The chamber, which simulates “free field” conditions, allows us to conduct extremely precise audio testing in accordance with industry standards.
The purpose of an anechoic chamber is to simulate “free field” conditions, in order to conduct acoustic measurements without the results being affected by the chatter of the cafeteria, by the highway roaring nearby, or—last but not least—by the room itself.
To absorb acoustic reflections, every inch of the internal walls is covered with 800mm pearl-gray melamine wedges that are capable of breaking sound waves by trapping them before they get a chance to bounce back towards the room.The floor floats on some sixty vibration-damping pads, called bushings or shock mounts. This system helps isolate the room from solidian noise—in other words, from structure-borne vibrations.
Finally, 200mm-thick walls composed of steel and various types of stone wool minimize airborne sound. While the exterior shell sits atop 28 square meters of shock mounts, the interior surface, factoring in the melamine wedges, offers about 10 square meters of treasured quietude for the measurements to come. Here’s a timelapse of the construction process:

 DSLR & Mirrorless
DSLR & Mirrorless  3D Camera
3D Camera  Drone & Action camera
Drone & Action camera 
